- Girgaon, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400004
- +91 8779472523/ 9561715438
- rashi91@gmail.com
Happy Hormones, Healthy Life!
Specialities
Endocrine Tumors
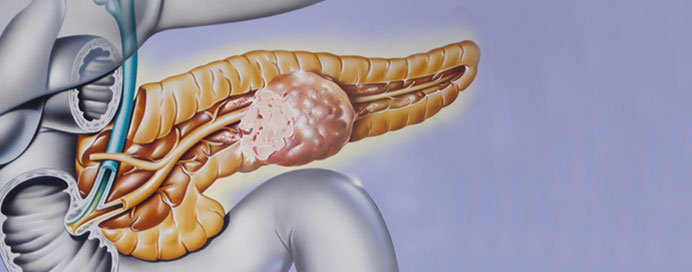
Endocrine tumors are abnormal growths that develop in the hormone-producing glands of the endocrine system, which includes the thyroid, adrenal, pituitary, and pancreatic islet cells, among others. These tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) and can significantly affect hormone levels, leading to a variety of symptoms depending on the gland involved and the hormones produced. For instance, a pheochromocytoma in the adrenal gland can cause excessive production of adrenaline, leading to high blood pressure, rapid heart rate, and anxiety, while a thyroid nodule could disrupt metabolism. Endocrine tumors often present with symptoms like unexplained weight changes, fatigue, changes in blood pressure, and glucose metabolism disorders. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of hormone level tests, imaging studies such as CT scans or MRIs, and biopsy procedures. Treatment options vary widely and may include surgical removal of the tumor, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and targeted drug treatments. Early detection and accurate diagnosis are crucial for effective management and improving patient outcomes, as these tumors can profoundly impact overall health and endocrine function.
